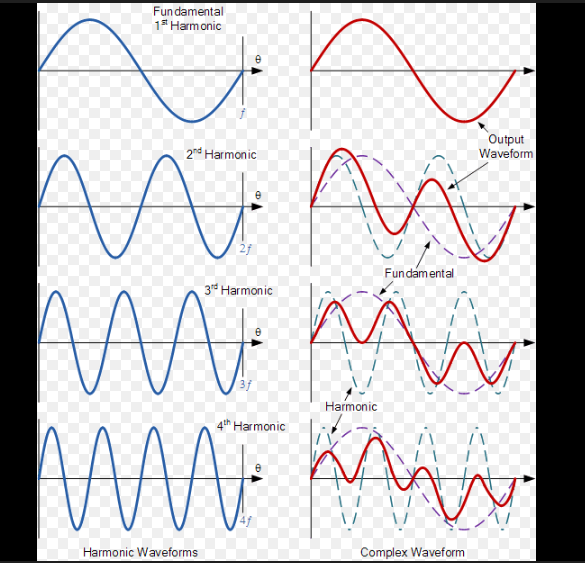
Harmonic Analysis
Electrical systems a large number of loads such as VFDs, UPS systems, computers, LED lights, and other electronic devices draw current in a non-linear manner. This creates waveform distortion in the network, commonly known as harmonics.
Harmonic Analysis to measure and understand these distortions and ensures the system meets acceptable power quality standards.
What Are Harmonics?
Harmonics are unwanted higher-frequency currents and voltages produced by non-linear loads.
Instead of drawing current smoothly, these loads take current in pulses, which distorts the normal sinusoidal waveform.
Common sources of harmonics include:
- Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs)
- UPS and rectifier units
- Solar and battery inverters
- LED lighting systems
- Computers and office equipment
- Welders and battery chargers
As these loads increase, harmonic distortion also rises.
Why Do We Need Harmonic Analysis?
Harmonic Analysis is important because high harmonic levels can cause several problems in electrical systems:
- Overheating of transformers, cables, and switchgear
- Nuisance tripping of breakers
- Malfunction of protection relays
- Reduced efficiency of motors
- Extra losses and heating
- Resonance issues with capacitor banks
- Premature failure of sensitive equipment
This study also checks compliance with IEEE 519, which defines allowable limits for harmonic distortion.
How Harmonic Analysis Is Carried Out
The study is usually done by modelling the electrical network and running harmonic simulations.
The main steps include:
- Collecting details of loads, especially non-linear loads
- Building the system model with transformers, cables, and sources
- Calculating current and voltage harmonics at important buses
- Checking Total Harmonic Distortion (THD) against limits
- Identifying any resonance conditions
- Suggesting solutions where THD is high
Understanding THD (Total Harmonic Distortion)
THD is the most common indicator of harmonic levels.
- Voltage THD (VTHD): Should generally be below 5%
- Current THD (ITHD): Depends on the size and strength of the system
Impact of Harmonics on Electrical Equipment
Harmonics can affect many parts of the system, such as:
- Transformers: Extra heating and reduced life
- Cables: Higher current and insulation stress
- Capacitor Banks: Risk of resonance and damage
- Motors: Reduced efficiency and torque issues
- Generators: Higher temperature and reduced performance
- Relays: Incorrect operation or mis-tripping
Solutions to Reduce Harmonics
Different solutions can be used depending on how high the distortion is:
- Passive harmonic filters
- Active harmonic filters
- Detuned capacitor banks
- Line reactors or chokes
- Multi-pulse VFDs (12-pulse, 18-pulse)
- Isolation transformers
- Phase-shift transformers
Conclusion
Harmonic Analysis plays an important role in maintaining good power quality. The waveform distortion, avoid equipment failures, reduce losses, and ensure compliance with standards like IEEE 519.With the growing use of non-linear loads, harmonic studies