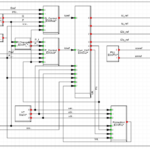
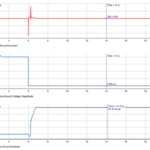
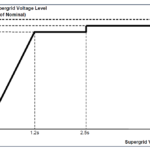
Short circuit withstand capacity
The protective devices like fuses and circuit breakers protecting cable and other electrical equipment against short circuit faults operate after lapse of certain time. Any cable must be able to withstand the maximum expected and calculated short circuit current in its circuit for fault clearing time without exceeding the maximum permissible conductor temperature. Short circuit withstand and capacities in kilo-amperes are given for various cable sizes by cable manufactures in standard tables from which one has to select proper size depending upon the system short circuit rating and permissible fault clearing time.
During a short circuit, a high amount of current can flow through a cable for a short time. This surge in current flow causes a temperature rise within the cable. High temperatures can trigger unwanted reactions in the cable insulation, sheath materials and other components, which can prematurely degrade the condition of the cable. As the cross-sectional area of the cable increases, it can dissipate higher fault currents for a given temperature rise. Therefore, cables should be sized to withstand the largest short circuit that it is expected to see.
The minimum cable size due to short circuit temperature rise is typically calculated with an equation of the form:
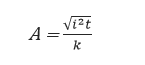
Where,
A is the minimum cross-sectional area of the cable ![]()
i is the prospective short circuit current (A)
t is the duration of the short circuit (s)
k is a short circuit temperature rise constant
The temperature rise constant is calculated based on the material properties of the conductor and the initial and final conductor temperatures.
For copper cables:
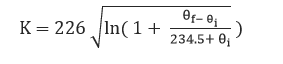
For aluminum cables:
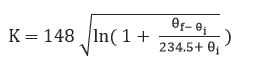
Where,
![]() and are the initial and final conductor temperatures respectively.
and are the initial and final conductor temperatures respectively.
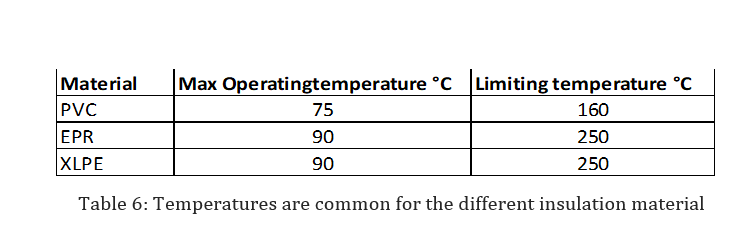
The following temperatures are common for the different insulation materials
Enquiry preparation and order specification:
- Low and medium voltage cable enquiry shall be prepared.
- For package always use 3.5 core cables
- Specify only extruded cables
- Cable estimation for each length shall be accurately with 5% margin on higher side.
- With order specification, depending on length, especially for higher size of cables drum length schedule can be given
- Also changes taken place during the course of engineering shall be accounted.
Example 1:
Motor rating = 90KW
Full load current = 157
De-rating factor:
- Rating factor for variation in depth of laying in ground = 0.97
- Group rating factor for multi-core formation and laid direct in the ground =0.48
- Rating factor for variation in ground temperature = 0.94
- Rating factor for variation in thermal resistivity of soil = 1.0
De-rating factor for cable is laid in air and also in trench = 0.97 x 0.48 x 094 x 1.0
= 0.44
Therefore, the cable should have current rating of 157 A
3.5 core x 185 Sq.mm cable has current rating = 200 A in duct
We are using 2 runs of 3.5 C x 185 Sq.mm cable
The total capacity = 2 x 200 = 400 A (which is more than 356.82 A)
Thus 2 runs of 3.5C x 185 Sq. mm cable are adequate.
Full load current = 157 A
(Starting p.f = 0.3) = 1130A
Phase = 72.54°
We have selected 2 runs of 3.5 C x 185 ![]()
R = 0.199 Ω/km
X = 0.082 Ω/km
Power factor cos ⍬ = 0.8
⍬ = 36.27°
Voltage drop during starting:
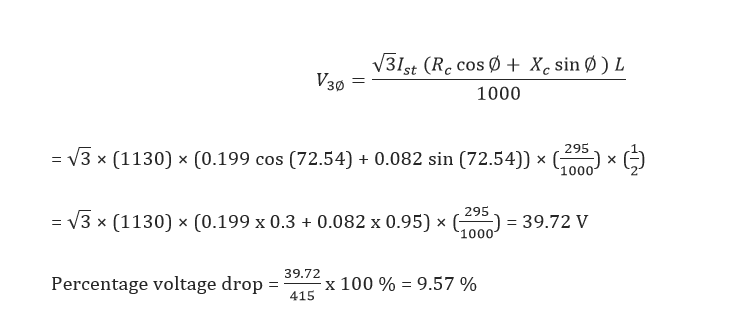
Voltage drop during running:
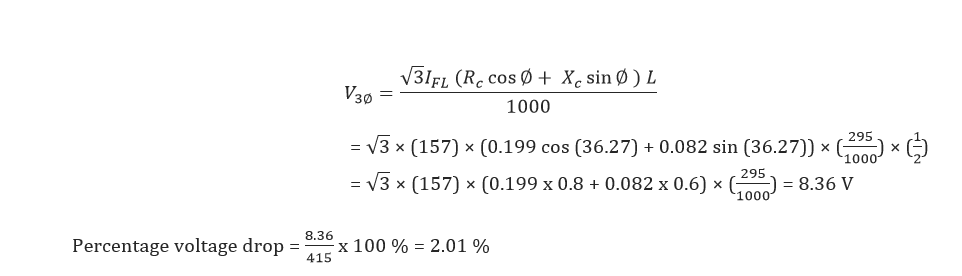
Thus the voltage drops in cable during starting & running condition are within permissible limits.
(Permissible limits-less than 5 %)
Example 2: Medium voltage cable 11/33 KV
Load = 2MVA
FLA = 105 kA
Considering de-rating factor as same as in example 1, de-rating factor is 0.44
Therefore, the cable should have current rating of 105 A
3.5 core x 185 Sq.mm cable has current rating = 200 A in duct
Thus 1 runs of 3.5C x 185 Sq. mm cable are adequate.
We have selected 1 runs of 3.5 C x 185
R = 0.199 Ω/km
X = 0.082 Ω/km
Power factor cos ⍬ = 0.8
⍬ = 36.27°
Voltage drop during normal condition:
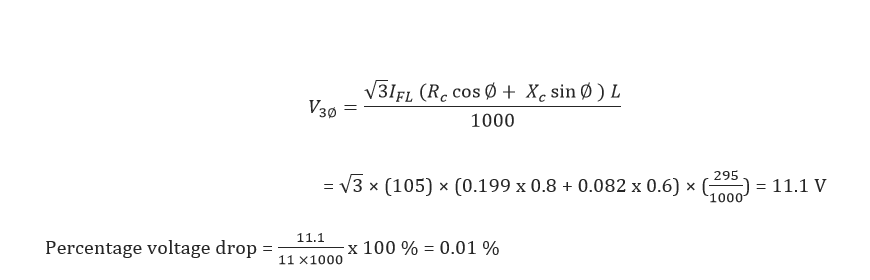
Thus the voltage drops in cable during normal condition within permissible limits.