High Voltage Ride Through (HVRT)
What is HVRT?
High Voltage Ride Through (HVRT) means the ability of a power plant to stay connected to the grid during short-term high voltage conditions (over-voltage). During such events, the plant should not trip immediately, because the voltage rise is temporary and the system normally returns to normal within seconds.
HVRT is mandatory for:
Solar power plants
Wind power plants
Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS)
Why is HVRT Important?
High Voltage Ride Through (HVRT) helps the grid remain stable during temporary voltage rise events.
If many plants trip together during an over-voltage:
Grid voltage becomes more unstable
Large generation loss can occur suddenly
Risk of cascading trips increases
System collapse and blackout risk increases
So, most grid codes require ride-through operation instead of immediate tripping.
When Does High Voltage Occur?
High voltage usually happens due to:
Sudden load rejection (load is removed, voltage rises)
Clearing of transmission line faults (voltage overshoot after fault clearance)
Switching of capacitor banks or reactors
Lightly loaded networks or weak grids
These are temporary events, not permanent faults.
What Should the Plant Do During HVRT?
During high voltage:
The plant must stay connected
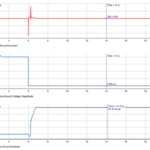
Active power output may be reduced temporarily
Reactive power is absorbed (to help reduce voltage)
The controller supports voltage recovery as per grid code
After voltage returns to normal:
The plant resumes normal operation automatically
Active/reactive power returns to normal within the allowed recovery time
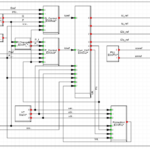
This response is handled by the inverter controller and plant controller (PPC) based on the HVRT settings.
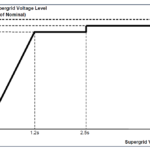
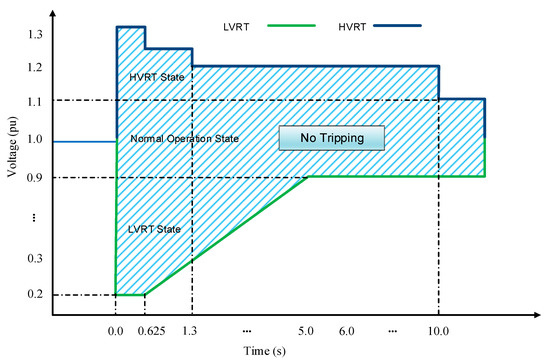
HVRT Voltage–Time Requirement
Grid codes define how long the plant must stay connected depending on the voltage level.
| Voltage Level | Ride-Through Requirement |
|---|---|
| Up to 1.10 pu | Continuous operation |
| 1.20 pu | At least 1 second |
| 1.30 pu | At least 0.2 second |
| Above limit | Tripping allowed |
Conclusion
High Voltage Ride Through (HVRT) is an essential grid requirement for modern power plants.
It ensures that solar, wind, and BESS plants remain connected during short-term over-voltage conditions. Instead of tripping, the plant supports the grid by absorbing reactive power and reducing active power. This improves reliability and prevents sudden loss of generation during voltage disturbances.