Arc Flash Analysis
Arc Flash Analysis is an essential electrical safety assessment used to identify arc flash hazards and determine incident energy levels in power systems. This study improves worker safety by defining PPE requirements, setting safe working boundaries, applying warning labels, and recommending risk reduction measures to minimize injuries and equipment damage.
Arc Flash Study Overview
An arc flash occurs when electrical current leaves its intended path and travels through the air between energized conductors or between a conductor and earth. This can happen due to loose terminations, insulation failure, dust or moisture inside panels, equipment ageing, or accidental contact with tools and foreign objects.
During an arc flash event, temperatures can rise extremely high within milliseconds. As a result, metal parts may melt, pressure waves may form, and intense light and sparks may spread outward. These conditions create serious hazards such as severe burns, hearing damage, and potential fatalities.
How Arc Flash Analysis Is Performed
1. System Modeling
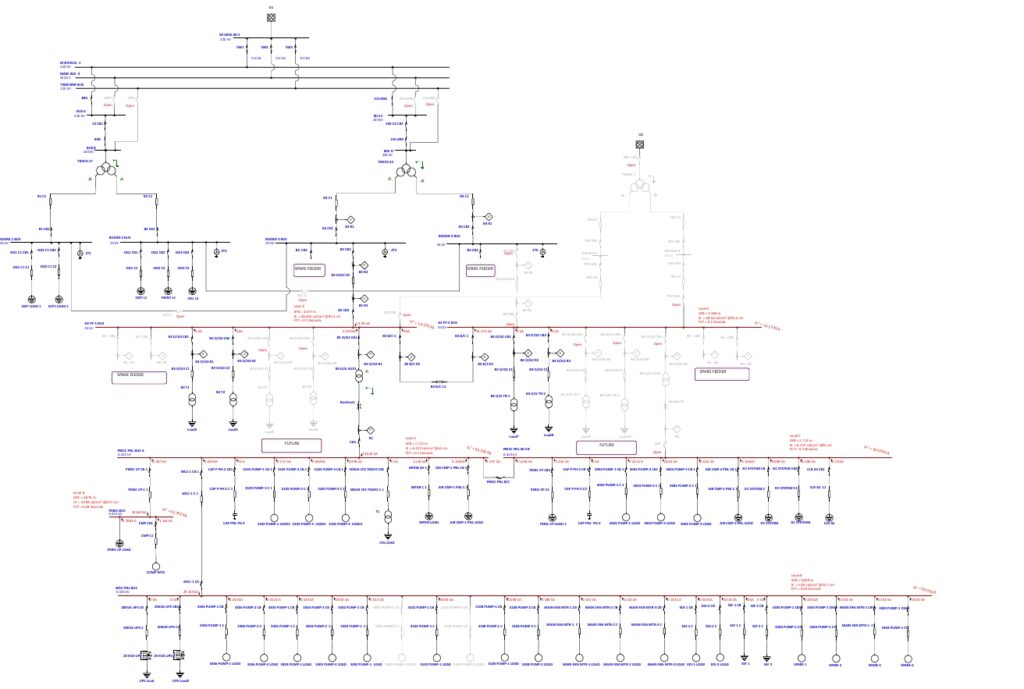
Prepare the complete electrical network model including transformers, switchgear, cables, motors, breakers, relays, and earthing system details.
2. Short-Circuit Calculations
Calculate the available fault current at each bus for both maximum and minimum operating conditions.
3. Protection Coordination Review
Verify that relays and breakers operate in the correct sequence and clear faults quickly to reduce arc duration.
4. Incident Energy Calculation
Use IEEE 1584-2018 equations to calculate the incident energy (heat exposure) released during an arc fault.
5. Arc Flash Labels
Provide labels on electrical equipment showing critical safety details such as:
Incident energy value (cal/cm²)
Arc flash boundary
Working distance
Required PPE category
Nominal system voltage and available fault current
Why Arc Flash Analysis Is Essential
Arc flash analysis helps to understand how much heat and energy can be released during a fault and how far the hazard can spread. The study provides:
Incident Energy Levels
Measured in cal/cm², used to decide the severity of burns and PPE needed.
Arc Flash Boundary
The distance at which a worker may be exposed to 1.2 cal/cm² of energy.
Required PPE Category
Specifies the arc-rated clothing and protective equipment workers must use.
Trip Times of Protection Devices
Ensures relays and breakers operate quickly to reduce incident energy.
Compliance with Standards
Meets the requirements of IEEE 1584-2018, NFPA 70E, and IEC 61482.
Arc flash analysis improves safety at the workplace and reduces the chance of major equipment failures.
Conclusion
Arc flash hazards present major risks in electrical systems; however, these risks can be significantly reduced through a detailed Arc Flash Study. By identifying hazards, improving protection performance, ensuring compliance with safety standards, and enhancing system reliability, organizations can create a safer working environment and reduce the chance of serious accidents.